论文标题:Thrombin@Fe3O4 nanoparticles for use as a hemostatic agent in internal bleeding
期刊:Scientific Reports
作者:Emiliya M. Shabanova, Andrey S. Drozdov, Anna F. Fakhardo, Ivan P. Dudanov, Marina S. Kovalchuk, Vladimir V. Vinogradov
发表时间:2018/01/10
数字识别码:10.1038/s41598-017-18665-4
原文链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-18665-4?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-MixedBrand-multijournal-Multidisciplinary-China&utm_campaign=ORG_USG_JRCN_RL_article_promotion_sciencenet_Oct_3rd
出血是导致过早死亡的主要因素之一,而内出血是其中最危险的出血类型。
近日,在《科学报告》发表的一篇名为Thrombin@ Fe3O4 nanoparticles for use as a hemostatic agent in internal bleeding的文章里,来自俄罗斯圣彼得堡国立信息技术机械与光学大学的Vladimir V. Vinogradov 的团队第一次使用止血磁性纳米颗粒来进行内出血微创治疗,即将纳米颗粒直接导入循环系统,然后利用外加磁场来定位流血区域。纳米颗粒的制备是通过将人凝血酶(THR)包埋到由溶胶-凝胶法制备的磁铁矿结构中,然后研磨至200nm以下,最后进行胶体化。制成的胶体在体外实验环境下,展现了凝血效果,引起了血浆的凝固。
Vinogradov 的团队还利用血管模型展示了,凝血酶@铁化合物因为活性较低,不会引起系统性血栓形成,但如果施加外加磁场使其聚集,同时注射纤维蛋白原,则会加速局部止血速度。作者使用带有穿孔的血管模型,穿孔区域有循环血液流动,施加了永久磁场之后,止血速度是对比组的6.5倍。作者还对样品进行了生物相容性实验,HELF 和HeLa细胞均未展现毒性效应。
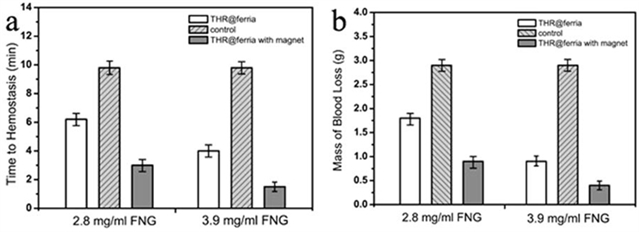
图1:不同实验组凝血时间和失血量对比图。
摘要:Bleeding remains one of the main causes of premature mortality at present, with internal bleeding being the most dangerous case. In this paper, magnetic hemostatic nanoparticles are shown for the first time to assist in minimally invasive treatment of internal bleeding, implying the introduction directly into the circulatory system followed by localization in the bleeding zone due to the application of an external magnetic field. Nanoparticles were produced by entrapping human thrombin (THR) into a sol-gel derived magnetite matrix followed by grinding to sizes below 200 nm and subsequent colloidization. Prepared colloids show protrombotic activity and cause plasma coagulation in in vitro experiments. We also show here using a model blood vessel that the THR@ferria composite does not cause systematic thrombosis due to low activity, but being concentrated by an external magnetic field with simultaneous fibrinogen injection accelerates local hemostasis and stops the bleeding. For instance, a model vessel system with circulating blood at the puncture of the vessel wall and the application of a permanent magnetic field yielded a hemostasis time by a factor of 6.5 shorter than that observed for the control sample. Biocompatibility of composites was tested on HELF and HeLa cells and revealed no toxic effects.
阅读论文全文请访问:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-18665-4?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-MixedBrand-multijournal-Multidisciplinary-China&utm_campaign=ORG_USG_JRCN_RL_article_promotion_sciencenet_Oct_3rd
期刊介绍:Scientific Reports (https://www.nature.com/srep/) is an online, open access journal from the publishers of Nature. We publish scientifically valid primary research from all areas of the natural and clinical sciences.
The 2017 journal metrics for Scientific Reports are as follows:
•2-year impact factor: 4.122
•5-year impact factor: 4.609
•Immediacy index: 0.576
•Eigenfactor® score: 0.71896
•Article Influence Score: 1.356
•2-year Median: 2
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。