|
|
|
|
|
CAR T细胞治疗火热,其靶向生物标志物的研究呈指数级增长态势 | BMC Journal |
|
|
论文标题:The expansion of targetable biomarkers for CAR T cell therapy
期刊:Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research
作者:Michelle H. Townsend, Gajendra Shrestha, Richard A. Robison and Kim L. O’Neill
发表时间:2018/07/21
数字识别码:10.1186/s13046-018-0817-0
原文链接:https://jeccr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13046-018-0817-0?utm_source=BMC_mailing&utm_medium=Email_Internal&utm_content=EvaFon-BMC-Journal_of_Experimental_and_Clinical_Cancer_Research-Oncology-Global&utm_campaign=AJH_AWA_JECCR_10th_Anniversary#Abs1
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Dv_7Rvn3DMdlwoav6uLN6Q
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research于7月发表了一篇综述:The expansion of targetable biomarkers for CAR T cell therapy。作者讨论了目前研究较多的CAR T靶向生物标志物,并着重指出一些未来将有望成为治疗靶点的生物标志物。
生物标志物可用于肿瘤风险评估、筛查、鉴别诊断、预后判断、疗效预测以及疾病进展的监测,是肿瘤治疗不可或缺的一部分。最近,随着嵌合抗原受体(CAR)T细胞疗法的出现,人们发现了一类新的靶向生物标志物。这些生物标志物多在肿瘤细胞表面,可作为细胞毒性T细胞的靶点。

图1 癌症生物标志物的应用图源:Kim L. O’Neill 等
首个用于CAR T细胞治疗的靶向生物标志物为CD19,这是一种在恶性B细胞上高度表达的B细胞标志物。随着CD19的成功发现,在过去的十年中,又在一系列人类恶性肿瘤中发现了大量新的靶向生物标志物。

图2:目前在临床试验中用到的CAR T细胞
它们的出现使得人们开展定向的、特定的治疗成为可能,从而减少了对健康组织的破坏,并尽可能在治疗期间保护了患者的免疫系统。
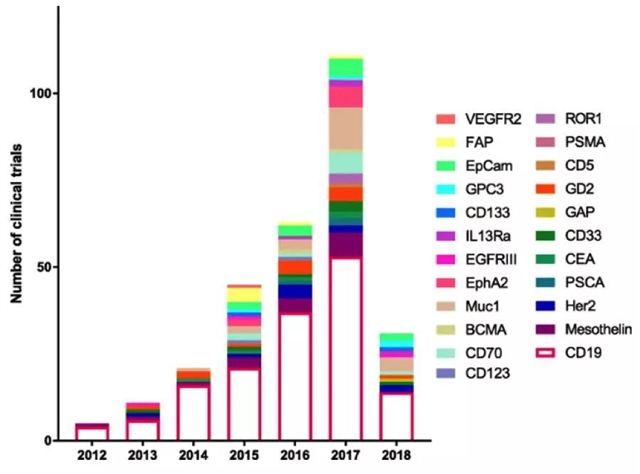
图3:截至2018年5月在临床实验中用到的生物标志物种类剧增、数量呈指数增长
截至2018年5月,共有100多项临床试验正在进行,涉及的表面生物标志物超过25种,研究几乎涵盖了人体的每种组织。大量临床试验的开展不仅在患者临床结局方面带来了可喜的结果,同时也使得探索可用于CAR T治疗的新型生物标志物的研究数量呈现指数级增长。
摘要:Biomarkers are an integral part of cancer management due to their use in risk assessment, screening, differential diagnosis, prognosis, prediction of response to treatment, and monitoring progress of disease. Recently, with the advent of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cell therapy, a new category of targetable biomarkers has emerged. These biomarkers are associated with the surface of malignant cells and serve as targets for directing cytotoxic T cells. The first biomarker target used for CAR T cell therapy was CD19, a B cell marker expressed highly on malignant B cells. With the success of CD19, the last decade has shown an explosion of new targetable biomarkers on a range of human malignancies. These surface targets have made it possible to provide directed, specific therapy that reduces healthy tissue destruction and preserves the patient’s immune system during treatment. As of May 2018, there are over 100 clinical trials underway that target over 25 different surface biomarkers in almost every human tissue. This expansion has led to not only promising results in terms of patient outcome, but has also led to an exponential growth in the investigation of new biomarkers that could potentially be utilized in CAR T cell therapy for treating patients. In this review, we discuss the biomarkers currently under investigation and point out several promising biomarkers in the preclinical stage of development that may be useful as targets.
阅读论文全文请访问:https://jeccr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13046-018-0817-0?utm_source=BMC_mailing&utm_medium=Email_Internal&utm_content=EvaFon-BMC-Journal_of_Experimental_and_Clinical_Cancer_Research-Oncology-Global&utm_campaign=AJH_AWA_JECCR_10th_Anniversary#Abs1
期刊介绍:Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (https://jeccr.biomedcentral.com/) is an online peer-reviewed journal that publishes original research papers, reviews and commentaries in cancer research, from bench to bedside.
2017 Journal Metrics
Citation Impact
6.217 - 2-year Impact Factor
5.280 - 5-year Impact Factor
1.350 - Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP)
2.000 - SCImago Journal Rank (SJR)
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。