|
|
|
|
|
FESE | 前沿研究:无锡市生活/工业混合污水处理厂微塑料分布、特征及日变化趋势 |
|
|
论文标题:Distribution, characteristics and daily fluctuations of microplastics throughout wastewater treatment plants with mixeddomestic–industrial influents in Wuxi City, China. (无锡市生活/工业混合污水处理厂微塑料分布、特征及日变化趋势)
期刊:Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering
作者:Wei Shan , Bingbing Li , Haichuan Zhang , Zhenghao Zhang , Yan Wang , ZhiyangGao , Ji Li
发表时间:29 Oct 2021
DOI:10.1007/s11783-021-1440-4
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章

原文链接(点击“阅读原文”直接获取)
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fese/EN/10.1007/s11783-021-1440-4
文章出版:Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16(1): 6
原文信息
题目:
Distribution, characteristics and daily fluctuations of microplastics throughout wastewater treatment plants with mixeddomestic–industrial influents in Wuxi City, China
作者:
Wei Shan 1, Bingbing Li ( )1, Haichuan Zhang 1, Zhenghao Zhang 1, Yan Wang 1,3, ZhiyangGao 4, Ji Li (
)1, Haichuan Zhang 1, Zhenghao Zhang 1, Yan Wang 1,3, ZhiyangGao 4, Ji Li ( ) 1,2
) 1,2
作者单位:
1 Jiangnan University, China
2 Jiangsu College of Water Treatment Technology and Material Collaborative Innovation Centre, China
3 Wuxi Puhui Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd., China
4 Wuxi Hi-Tech Water Co., Ltd., China
通讯作者邮箱:
[email protected] (B. Li);
[email protected] (J. Li)
关键词:
Microplastic (微塑料);
Wastewater treatment plant (污水处理厂);
Mixeddomestic-industrial influent (生活-工业混合进水);
Characteristic(特征) ;
Daily fluctuation (日变化)
文章亮点
• 对无锡市三个生活-工业混合污水处理厂MPs进行分析;
• 来自塑料制造的白色聚乙烯颗粒是最主要的MPs类型;
• MPs在随机抽样中数量要低于每日密集抽样;
• 需要从源头上限制微珠等MPs产品的生产。
文章简介
无处不在的微塑料(MPs)已在不同环境中被检测到。由于粒径小于5毫米,MPs可以通过各种水生动物的摄入进入到食物链。机械损伤、浸出的塑料添加剂以及来自MPs的活性氧或与MPs相关的吸附有毒污染物将对人类和动物健康构成潜在风险。污水处理厂(WWTPs)被认为是潜在的MPs来源且组成复杂,特别是在生活-工业混合WWTP中。
以前研究表明,污水处理厂进水中污染物浓度在一天内不断波动,且不同污水处理厂中MPs分布和特征差异很大。而传统的随机抽样可以大致描绘出MPs的分布和特征,但不能准确反映其每日波动情况。本研究采用显微-拉曼光谱分析了中国无锡市三个具有不同进水特性的生活-工业混合进水污水处理厂(W1、W2和W3)整个处理阶段的MPs浓度、形状、聚合物类型、尺寸和颜色,并通过密集抽样法获得了24小时内MPs的每日波动情况。
通过采用两种抽样策略,评估了三个WWTPs中MPs的分布、特征和日变化,分析了MPs浓度与水质参数之间的相关性。
(1)对于进水样品,W1的平均MP浓度为392.2个/L,占工业废水的10%,远远高于W2(71.2个/L,占工业废水10%)和W3(38.3个/L,占工业废水60%)。
(2)来自塑料制造业的直径小于0.5 mm的白色聚乙烯颗粒是W1的进水中最主要的MPs,证明了工业源在MPs污染中的关键作用。
(3)少量的MPs(小于4.0个/L)存在于这些WWTPs的出水中,归因于废水处理过程的有效去除。
(4)每日密集采样结果显示,W1进水中MP浓度一天内在29.1个/L和4617.6个/L之间大幅波动。
(5)此外,应开展长期的每日密集抽样活动以获得关于MPs更准确的信息,以及应进一步注意对MPs主要来源的监管。
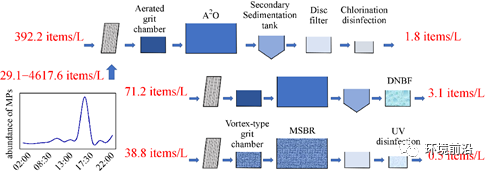
文章摘要图
编委点评
当前,废弃塑料在环境中的长期累积并带来的不良影响正在日益扩大,已经无处不在;2022年3月的联合国环境大会上签署了一项名为《终结塑料污染》的新决议,旨在终结塑料污染的蔓延。城镇污水处理厂被视为环境中微塑料的重要来源,但现阶段对其具体组成特征、排放量等信息的掌握仍然不足。该研究通过对典型污水处理厂详尽的采样调查,研究工作可以为准确评估人类活动微塑料向环境的输入提供重要基础数据。
编者 | 王琦瑞
点评 | 童银栋
致 谢
童银栋,天津大学教授,FESE青年编委;研究方向为流域氮磷过程模拟与水生态风险调控,主持自然科学基金优秀青年科学基金、面上等项目,以第一/通讯作者在Nat. Geosci.、PNAS、ES&T、Water Res.等杂志发表相关成果,个人主页:http://tjusee.tju.edu.cn/info/1151/1951.htm
王琦瑞,女,21岁,东北林业大学林学院2018级环境科学专业本科生,导师为肖鹏飞副教授,研究方向为环境修复材料的制备及在水处理中的应用研究。
摘要
In wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), microplastics (MPs) are complex, especially with mixed domestic–industrial influents. Conventional random grab sampling can roughly depict the distribution and characteristics of MPs but can not accurately reflect their daily fluctuations. In this study, the concentration, shape, polymer type, size, and color of MPs were analyzed by micro-Raman spectroscopy (detection limit of 0.05 mm) throughout treatment stages of three mixed domestic–industrial WWTPs (W1, W2, and W3) in Wuxi City, China, and the daily fluctuations of MPs were also obtained by dense grab sampling within 24 h. For influent samples, the average MP concentration of 392.2 items/L in W1 with 10% industrial wastewater was much higher than those in W2 (71.2 items/L with 10% industrial wastewater) and W3 (38.3 items/L with 60% industrial wastewater). White polyethylene granules with a diameter less than 0.5 mm from plastic manufacturing were the most dominant MPs in the influent of W1, proving the key role of industrial sources in MPs pollution. In addition, the daily dense sampling results showed that MP concentration in W1 influent fluctuated widely between 29.1 items/L and 4617.6 items/L within a day. Finally, few MPs (less than 4.0 items/L) in these WWTPs effluents were attributed to the effective removal of wastewater treatment processes. Thus, further attention should be paid to regulating the primary sources of MPs.
期刊简介

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中13种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。