法国图卢兹大学国家科学中心Léo Vacher课题组和意大利卡利亚里天文台Alessia Ritacco、法国巴黎高等师范学校等单位人员合作开展研究,经过不懈努力,他们揭示了基于普朗克HFI数据的尘埃偏振谱依赖性-宇宙微波背景偏振前景建模的转折点。该研究成果于2023年2月21日发表在国际一流学术期刊《天文学与天体物理学》杂志上。
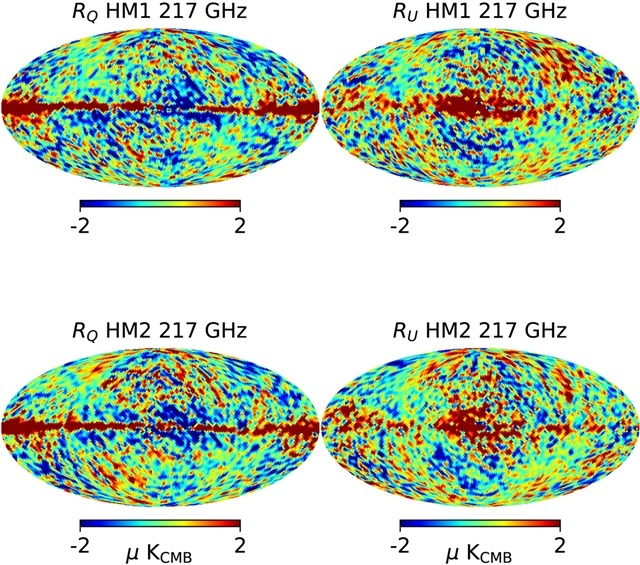
课题组利用新发布的SRoll2映射,对Planck数据进行功率谱分析,纠正了残余数据系统性误差,并将分析扩展到接近银河系平面的区域,相较于之前的研究有所改进。课题组的分析聚焦在最低的多极值(4和32之间),以及天区分数fsky分别为=80%、90%和97%的三个天区。极化的平均尘埃 SED和353 GHz Q和U映射被用于计算100、143和217 GHz的残差图,突出了尘埃极化SED在天空和沿视线的变化。在三个天区的三个频率上检测到残差。
研究小组表明,基于总强度数据的模型最终低估了(相差显著因子)极化CMB前景的复杂性。分析强调了需要包括偏振CMB前景偏振角度的变化。残差图的EE和BB功率谱的频率依赖性进一步提供了见解。研究小组发现,经修改的黑体(MBB)谱到一阶矩的展开提供了对EE功率谱的良好拟合。这一结果表明,残差主要可能来自尘埃MBB光谱参数的变化。
然而,这一结论受到交叉谱的挑战,交叉谱显示三个频率的残差映射不完全相关,以及BB功率谱与MBB SED的一阶矩展开不匹配。这项工作对尘埃极化前景和分量分离方法的模拟提出了新的要求,表明需要对尘埃建模进行重大改进,以确保在未来CMB实验所需的精度下对CMB原始B模进行无偏检测。此外,还需要进一步的工作来从理论上建模偏振角变化对残差图的EE和BB功率谱的影响。
据悉,探寻宇宙微波背景(CMB)原始B模式的研究,需要将其与较明亮的前景尘埃信号分离。在这种情况下,热尘埃偏振的光谱能量分布(SED)特性已成为重要的研究课题。
附:英文原文
Title: Dust polarization spectral dependence from Planck HFI data - Turning point for cosmic microwave background polarization-foreground modeling
Author: Alessia Ritacco, Franois Boulanger, Vincent Guillet, Jean-Marc Delouis, Jean-Loup Puget, Jonathan Aumont, Léo Vacher
Issue&Volume: 2023/02/21
Abstract: The search for the primordial B-modes of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) relies on the separation from the brighter foreground dust signal. In this context, the characterization of the spectral energy distribution (SED) of thermal dust in polarization has become a critical subject of study. We present a power-spectra analysis of Planck data, which improves upon previous studies by using the newly released SRoll2 maps that include corrections on residual data systematics and by extending the analysis to regions near the Galactic plane. Our analysis focuses on the lowest multipoles between =4 and 32, as well as three sky areas with sky fractions of fsky=80%, 90%, and 97%. The mean dust SED for polarization and the 353 GHz Q and U maps are used to compute residual maps at 100, 143, and 217 GHz, highlighting variations of the dust polarization SED on the sky and along the line of sight. Residuals are detected at the three frequencies for the three sky areas. We show that models based on total-intensity data end up underestimating (by a significant factor) the complexity of dust polarized CMB foreground. Our analysis emphasizes the need to include variations of the polarization angles of the dust polarized CMB foreground. The frequency dependence of the EE and BB power spectra of the residual maps yields further insight. We find that the moments expansion to the first order of the modified black-body (MBB) spectrum provides a good fit to the EE power-spectra. This result suggests that the residuals could follow mainly from variations of the dust MBB spectral parameters. However, this conclusion is challenged by cross-spectra showing that the residuals maps at the three frequencies are not fully correlated, as well as the fact that the BB power-spectra do not match the first order moment expansion of a MBB SED. This work sets new requirements for simulations of the dust-polarized foreground and component separation methods, showing that a significant refinement to the dust modeling is necessary to ensure an unbiased detection of the CMB primordial B-modes at the precision required by future CMB experiments. Further works would also be required to theoretically model the impact of polarization-angle variations on the EE and BB power spectra of residual maps.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202244269
Source: https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2023/02/aa44269-22/aa44269-22.html
