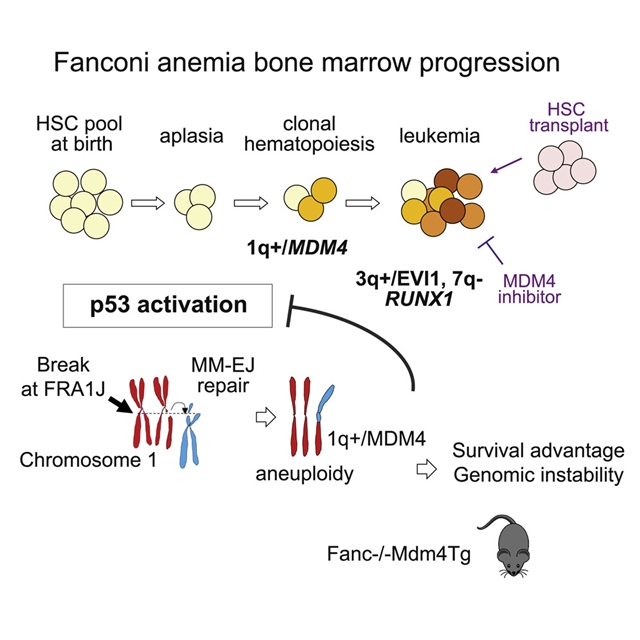
法国巴黎大学Jean Soulier和巴黎萨克雷大学Dominique Bluteau课题组合作取得一项新成果。经过不懈努力,他们的研究发现由染色体1q/MDM4三体诱导的克隆造血是范可尼贫血(FA)产生的典型途径。2023年2月2日,国际学术期刊《细胞—干细胞》发表了这一成果。
基于335名患者的纵向队列,研究人员对62名患者的克隆进化进行了临床、基因组和功能研究。研究人员发现了一种独特的体细胞结构变异和突变模式,其具有BRCA相关癌症的共同特征,FA的特点是不平衡、微同源介导的易位拷贝数改变。一半的患者出现染色体1q增益,通过MDM4三体下调p53信号传导驱动克隆造血,随后是继发性急性髓系低血病基因组改变。在功能上,MDM4三体使小鼠和人类原发性FA HSPC具有更大的适应性,挽救了炎症介导的骨髓衰竭,并推动了FA小鼠模型的克隆优势,同时在体外和体内靶向MDM4受损的白血病细胞。
该研究结果确定了继发性白血病生成的线性途径,其中早期MDM4诱导的p53激活下调起着关键作用,其具有预防和治疗前景。
据介绍,范可尼贫血患者的染色体不稳定导致造血干细胞/祖细胞(HSPC)衰竭,产生预后不良性髓系白血病。
附:英文原文
Title: Clonal hematopoiesis driven by chromosome 1q/MDM4 trisomy defines a canonical route toward leukemia in Fanconi anemia
Author: Marie Sebert, Stéphanie Gachet, Thierry Leblanc, Alix Rousseau, Olivier Bluteau, Rathana Kim, Raouf Ben Abdelali, Flore Sicre de Fontbrune, Loc Maillard, Carèle Fedronie, Valentine Murigneux, Léa Bellenger, Naira Naouar, Samuel Quentin, Lucie Hernandez, Nadia Vasquez, Mélanie Da Costa, Pedro H. Prata, Lise Larcher, Marie de Tersant, Matthieu Duchmann, Anna Raimbault, Franck Trimoreau, Odile Fenneteau, Wendy Cuccuini, Nathalie Gachard, Nathalie Auger, Giulia Tueur, Maud Blanluet, Claude Gazin, Michèle Souyri, Francina Langa Vives, Aaron Mendez-Bermudez, Hélène Lapillonne, Etienne Lengline, Emmanuel Raffoux, Pierre Fenaux, Lionel Adès, Edouard Forcade, Charlotte Jubert, Carine Domenech, Marion Strullu, Bénédicte Bruno, Nimrod Buchbinder, Caroline Thomas, Arnaud Petit, Guy Leverger, Gérard Michel, Marina Cavazzana, Eliane Gluckman, Yves Bertrand
Issue&Volume: 2023/02/02
Abstract: Fanconi anemia (FA) patients experience chromosome instability, yielding hematopoieticstem/progenitor cell (HSPC) exhaustion and predisposition to poor-prognosis myeloidleukemia. Based on a longitudinal cohort of 335 patients, we performed clinical, genomic,and functional studies in 62 patients with clonal evolution. We found a unique patternof somatic structural variants and mutations that shares features of BRCA-relatedcancers, the FA-hallmark being unbalanced, microhomology-mediated translocations drivingcopy-number alterations. Half the patients developed chromosome 1q gain, driving clonalhematopoiesis through MDM4 trisomy downmodulating p53 signaling later followed by secondary acute myeloid lukemiagenomic alterations. Functionally, MDM4 triplication conferred greater fitness to murine and human primary FA HSPCs, rescuedinflammation-mediated bone marrow failure, and drove clonal dominance in FA mousemodels, while targeting MDM4 impaired leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Our results identify a linear route toward secondary leukemogenesis whereby earlyMDM4-driven downregulation of basal p53 activation plays a pivotal role, opening monitoringand therapeutic prospects.
DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.01.006
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-stem-cell/fulltext/S1934-5909(23)00006-1
Cell Stem Cell:《细胞—干细胞》,创刊于2007年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:25.269
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-stem-cell/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-stem-cell/default.aspx
