美国约翰霍普金斯大学医学院Mei Wan团队近期取得重要工作进展,他们研究发现Oxylipin-PPARγ启动的脂肪细胞衰老在骨髓中传播继发性衰老。相关研究成果2023年4月4日在线发表于《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
据介绍,长期使用糖皮质激素会降低骨量和质量,增加骨髓肥胖,但其潜在机制尚不清楚。
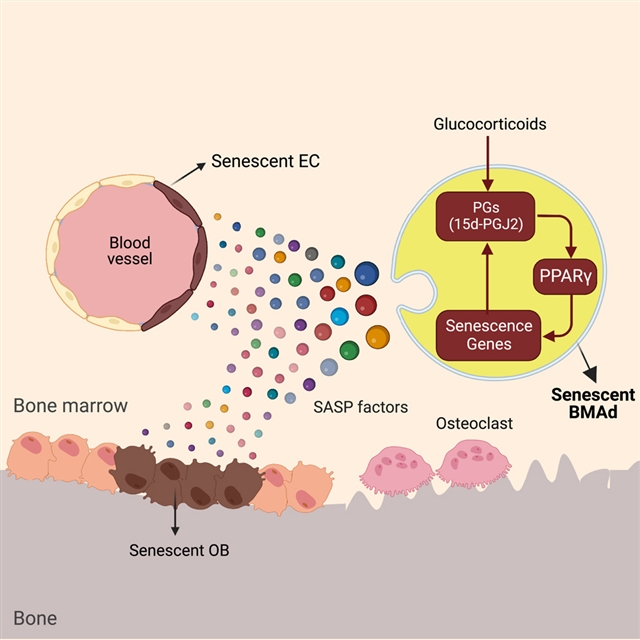
研究人员发现,成年小鼠的骨髓脂肪细胞(BMAd)谱系细胞在肾上腺糖皮质激素治疗后经历快速的细胞衰老。衰老的BMAd获得与衰老相关的分泌表型,从而在骨骼和骨髓中传播衰老。从机制上讲,糖皮质激素会增加oxylipin(如15d-PGJ2)的合成,用于过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(PPARγ)的激活。PPARγ刺激关键衰老基因的表达,也促进BMAd中oxylipin的合成,形成正反馈回路。将衰老的BMAd移植到健康小鼠的骨髓中足以诱导衰老细胞的二次扩散和骨丢失表型,而移植携带p16INK4a缺失的BMAd没有显示出这样的效果。
因此,糖皮质激素治疗诱导了一个脂质代谢回路,该回路有力地触发了BMAd谱系细胞的衰老,进而成为糖皮质激素诱导的骨退化的介质。
附:英文原文
Title: Oxylipin-PPARγ-initiated adipocyte senescence propagates secondary senescence in the bone marrow
Author: Xiaonan Liu, Yiru Gu, Surendra Kumar, Sahran Amin, Qiaoyue Guo, Jiekang Wang, Ching-Lien Fang, Xu Cao, Mei Wan
Issue&Volume: 2023/04/04
Abstract: The chronic use of glucocorticoids decreases bone mass and quality and increases bone-marrowadiposity, but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we show that bone-marrowadipocyte (BMAd) lineage cells in adult mice undergo rapid cellular senescence uponglucocorticoid treatment. The senescent BMAds acquire a senescence-associated secretoryphenotype, which spreads senescence in bone and bone marrow. Mechanistically, glucocorticoidsincrease the synthesis of oxylipins, such as 15d-PGJ2, for peroxisome proliferator-activatedreceptor gamma (PPARγ) activation. PPARγ stimulates the expression of key senescencegenes and also promotes oxylipin synthesis in BMAds, forming a positive feedback loop.Transplanting senescent BMAds into the bone marrow of healthy mice is sufficient toinduce the secondary spread of senescent cells and bone-loss phenotypes, whereas transplantingBMAds harboring a p16INK4a deletion did not show such effects. Thus, glucocorticoid treatment induces a lipidmetabolic circuit that robustly triggers the senescence of BMAd lineage cells that,in turn, act as the mediators of glucocorticoid-induced bone deterioration.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.005
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(23)00083-9
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
