|
|
|
|
|
FoAR 高密度城区口袋公园建设潜力评估与实施策略——以大连市为例 |
|
|
论文标题:Potential evaluation and implementation strategy for pocket park construction in high-density urban areas: A case study in Dalian, China
期刊:Frontiers of Architectural Research
作者:Jing Dong, Ruonan Guo, Fei Guo, Jun Cai
发表时间:April 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foar.2023.12.007
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章

FoAR是由高等教育出版社和东南大学建筑学院联合主办的全英文学术期刊
建筑学 / 城乡规划 / 风景园林
本刊已被 A&HCI / CSCD / Scopus / DOAJ / CSTPCD 收录

01 论 文 题 目
Manuscript Title
Potential evaluation and implementation strategy for pocket park construction in high-density urban areas: A case study in Dalian, China
高密度城区口袋公园建设潜力评估与实施策略——以大连市为例
02 作 者
Authors
Jing Dong, Ruonan Guo, Fei Guo*, Jun Cai
School of Architecture and Fine Art, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China
03 论 文 摘 要
Abstract
As an important element of urban renewal in highly urbanized areas, pocket parks with small size, flexible layout and daily accessibility are becoming a major component of green infrastructure and the mainstay of outdoor recreation space expansion in high-density urban centers. Nevertheless, the absence of a comprehensive framework for evaluating the potential of pocket park construction (PPC), one that integrates diverse influencing factors on a macro scale, has resulted in the random installation of such spaces, often failing to optimize the utilization of urban land. Addressing this critical lacuna, we propose an approach to evaluate PPC potential from a city-scale perspective, which is used to support the determination of which land units should be prioritized for PPC. A complete and feasible workflow was also established to identify potential land units, construct an index system for PPC combining demand and supply levels, quantitatively calculate indices based on remote sensing (RS) and geographic information system (GIS), accurately evaluate PPC potential using an entropy-weighted TOPSIS model, and develop targeted renewal strategies. A case study in Dalian, China, demonstrated the applicability and implications of the workflow. The results showed that it is flexible and easy to adapt to different local contexts, allowing evaluators to introduce parameters considering the availability of local data, and will help decision makers to build pocket parks in the most effective plots, providing a strong reference for high-quality development in other high-density urban centers facing the contradiction between ecological construction and land scarcity.
作为高度城市化地区城市微更新的重要内容,面积小、布局灵活、日常可达的口袋公园正逐渐成为高密度城市中心区绿色基础设施的主要组成部分和户外游憩空间拓展主体。然而目前对于城市口袋公园的空间规划问题研究尚不多见,由于缺乏从宏观尺度综合衡量不同影响因素的潜力评估框架,导致口袋公园随机建设,没有最大化城市土地价值。为了解决这个问题,我们从宏观尺度提出了一种评估城市口袋公园建设潜力的方法,用于支持确定哪些用地单元应被优先考虑建设口袋公园。还建立了一个完整可行的工作流程,以结合需求和供给层面构建口袋公园建设潜力评估指标体系,基于RS、GIS等方法定量计算指标,采用熵权TOPSIS模型开展潜力分级评估,从而得出用地单元的更新改造优先权,分类提出针对性更新策略。在中国大连一个典型的高密度城市中心区进行的案例研究证明了该工作流程的适用性和意义。结果表明,该方法很容易适应不同的当地环境,允许评估人员考虑当地数据的可用性确定相关参数,将帮助决策者在最有效的地块建设口袋公园,为面临生态建设与土地资源紧缺矛盾突出的其他高密度城市中心区的高质量发展提供了有力的参考。
04 关 键 词
Keywords
Pocket park / 口袋公园
Potential evaluation / 潜力评估
Urban renewal / 城市更新
High-density urban areas / 高密度城区
05 章 节 标 题
Sections Title
1. Introduction / 引言
2. Study area / 研究区域
3. Methodology / 研究方法
3.1. Data sources / 数据来源
3.2. Identification of potential land units / 潜在用地单元界定
3.3. Construction and calculation of index system / 指标体系构建量化
3.3.1. Factors affecting pocket park construction / 口袋公园建设影响因素
3.3.2. Construction of index system / 指标体系构建
3.3.3. Quantitative calculation of indices / 指标定量计算
3.4. Evaluation of PPC potential / 口袋公园建设潜力评估
3.4.1. Weight determination based on entropy weight method / 基于熵权法的权重确定
3.4.2. Potential evaluation based on TOPSIS / 基于TOPSIS的潜力计算
4. Results / 结果
4.1. Quantitative results of PPC potential indices / 口袋公园建设潜力指标量化
4.2. The potential evaluation and analysis of PPC / 口袋公园建设潜力评估分级
4.3. The implementation strategies of urban pocket parks / 城市口袋公园实施策略分析
4.3.1. Time-series strategies: implementation sequence based on potential evaluation / 时序策略:基于潜力分级的实施顺序制定
4.3.2. Spatial strategies: spatial design strategies for combining subjective and objective aspects / 空间战略:主客观结合的空间设计策略
5. Discussion / 讨论
5.1. Methods of PPC potential evaluation / 口袋公园建设潜力评估方法
5.2. Directions for future research / 未来研究方向
6. Conclusion / 结论
06 主 要 插 图
Illustrations

▲ 图一:研究区土地利用图。 © 本文作者
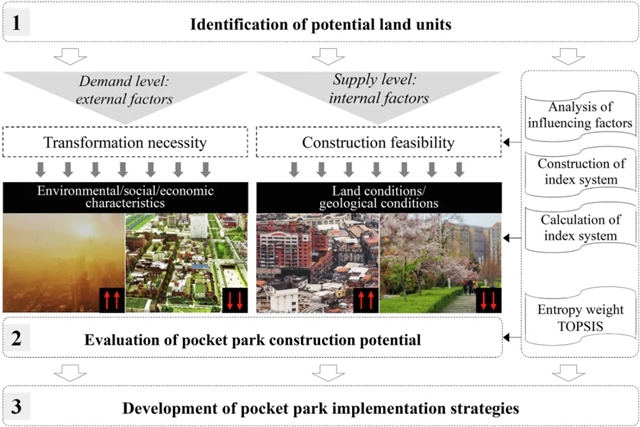
▲ 图二:研究方法的技术流程。 © 本文作者

▲ 图三:城市口袋公园建设潜力指标量化。 © 本文作者

▲ 图四:城市口袋公园建设潜力分级。 © 本文作者

▲ 图五:城市口袋公园建设潜力街道统计图。 © 本文作者

▲ 图六:本文的总体思路。 © 本文作者
07 作 者 介 绍
Authors’ Information

Jing Dong
Associate Professor
School of Architecture and Fine Art
Dalian University of Technology, China
Her research interests include ecological city planning, urban renewal, and resilient cities. To date, she has published over 30 papers, including 18 as the first/corresponding author in leading journals both at home and abroad in the fields of urban planning and ecology. She has led five projects, such as those funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, and provincial-level social science planning funds. Her accolades include a second prize for national excellence in urban and rural planning and design, a third prize for outstanding achievements in social sciences at the provincial and ministerial level, a first prize for excellence in urban and rural planning and design, and another third prize for the same category.

Ruonan Guo
Ph.D. Student
School of Architecture and Fine Art
Dalian University of Technology, China
As a second-year doctoral student, she is dedicated to exploring fields such as ecological urban planning, urban renewal, resilient cities, and urban thermal environments, aiming to make innovative contributions to sustainable urban development.

Fei Guo
Professor
School ofArchitecture and Fine Art
Dalian University of Technology, China
With a sustained focus on urban Design, urban climate, urban remote sensing, urban ventilation simulation, outdoor thermal comforts. As PI or Co-PI, Dr. Guo has been involved in 27 research projects receiving a total of ~RMB 3 millions from China research funding institutions (e.g. NFC, MOST and MOE) and enterprises since 2008. He has authored and co-authored more than 100 papers and book chapters. Published papers in academic journals: more than 15 English papers and more than 80 Chinese papers.

Jun Cai
Professor
School of Architecture and Fine Art
Dalian University of Technology, China
Professor at the School of Architecture and Fine Art, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China. His research interests include urban and rural transportation planning and land use planning. He has led three National Natural Science Foundation of China projects, published three academic monographs, and directed numerous projects.
08 原 文 阅 读
Download Link

长按上方二维码|浏览本期精彩论文
▼ 点击下方词条 | 往期精彩不容错过
#期刊快讯#系列
1/ 主编王建国院士团队荣获国家科技进步奖一等奖
2/ FoAR|2021年度报告,2022新年快乐!
3/ FoAR|2022年度报告,2023新年快乐!
4/ FoAR|2023年度报告,2024新年快乐!
5/ 最新|FoAR 2022 CiteScore 指数上升为4.7
6/ 2022年度JCR发布|FoAR 首获影响因子 3.5,位列建筑领域期刊第一
7/ 最新|FoAR 被中国科技论文与引文数据库(CSTPCD)收录
8/ 最新|FoAR 再次入选中国国际影响力优秀学术期刊
9/ 最新|FoAR 荣获科爱十大优秀期刊奖
10/ 最新|FoAR进入2023年中国科学院分区表1区
#新刊上线#系列
2024年第一期
2024年第二期
#FoAR投稿指南#系列
1/ 投稿流程
2/ Guide for Author中文版
3/ 审稿流程及发表流程
4/ 如何提交修改稿
5/ 录用文章出版流程
#期刊知识科普#系列
1/ SCI之父尤金·加菲尔德的传奇人生
2/ 国际核心期刊数据库大解析
3/ 手把手教你如何使用最强工具Web of Science
4/ 如何发现一本好期刊
5/ 国内核心期刊有哪些
6/ 版面费与期刊影响力
#精彩文章#系列精选
01/ 城市设计实践发展的多元维度——基于UAL的案例研究
02/ 从智慧城市到共情城市
03/ 传统阿拉伯伊斯兰城市居住区形态学:以传统城市大马士革为例
04/ 建筑遗产预防性保护的意大利视角
05/ 生物与建筑:将科学知识与设计实践相结合的六家法国建筑事务所项目案例研究
06/ 颇具争议的渐进式改造:Elemental建筑事务所金塔蒙罗伊公屋居住区项目的15年
07/ 联合眼动实验和SD法的传统商业街区视觉效果感知评价
08/ 历史的层次:古城堡遗迹中的新建筑改造
09/ 通过空间句法检验帕拉第奥别墅平面中的控制性、中心性和灵活性
10/ 自1931年柯布西耶的Salubra色卡问世后其建筑色彩的偏好:一种跨文化的分析
11/ 建筑师身份的描绘:1920年代末的中国美术建筑师——刘既漂
12/ 探索暴露于风影响下织物的表达与功能
13/ 绿色屋顶能否在地中海气候条件下显著节约能源?基于不同案例的批判性评估
14/ 芬兰近期落成的原木建筑的建构及建筑品质:相关建筑师的解读
15/ 新加坡高校教室光环境品质研究
《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。