论文标题:Sleep increases chromosome dynamics to enable reduction of accumulating DNA damage in single neurons
期刊:Nature Communications
作者:D. Zada, I. Bronshtein, T. Lerer-Goldshtein, Y. Garini, L. Appelbaum
发表时间:2019/03/05
数字识别码: 10.1038/s41467-019-08806-w
原文链接:http://t.cn/EMvfAt1
微信链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/AOIsYmJN16s-2s2LaVvO6Q
《自然-通讯》本周发表的一篇论文Sleep increases chromosome dynamics to enable reduction of accumulating DNA damage in single neurons报告了睡眠对活斑马鱼体内个体神经元的影响。研究发现,睡眠会增加染色体的运动(染色体动力学),从而改变染色体结构并减少DNA损伤。结果显示,染色体动力学可能是定义个体睡眠神经元的潜在标志物。

图1 图源:Pixabay
长期睡眠剥夺可以致命,睡眠障碍也与各种大脑功能缺陷有关。虽然研究人员已知睡眠非常重要,但对睡眠在细胞水平上的作用尚不清楚。这是因为此前无法用显微镜研究睡眠依赖性的细胞过程,只能通过行为学标准来定义睡眠。
以色列巴伊兰大学的Lior Appelbaum和同事报告了一种新方法,可以对活斑马鱼体内个体神经元的染色体动力学进行定时拍摄。作者运用该方法表明,睡眠可以让染色体动力学增加两倍,尤其是神经元中的染色体;而神经元活动则会产生相反的作用。作者指出,睡眠依赖的染色体动力学增加对于 DNA双链断裂的修复必不可少。
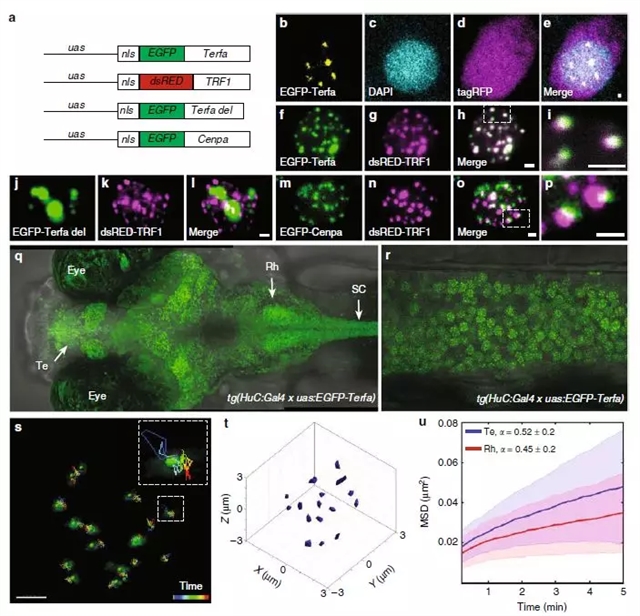
图2:拍摄活斑马鱼幼体的染色体动力学。图源:Zada等
虽然研究证明睡眠对神经元的维护具有关键作用,但也指出保持清醒和细胞活动会导致DNA损伤的积累。未来还需要对其它脊椎动物和无脊椎动物开展进一步研究,才能确定染色体动力学是否是细胞睡眠的一个演化保守的标志物。
摘要:Sleep is essential to all animals with a nervous system. Nevertheless, the core cellular function of sleep is unknown, and there is no conserved molecular marker to define sleep across phylogeny. Time-lapse imaging of chromosomal markers in single cells of live zebrafish revealed that sleep increases chromosome dynamics in individual neurons but not in two other cell types. Manipulation of sleep, chromosome dynamics, neuronal activity, and DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) showed that chromosome dynamics are low and the number of DSBs accumulates during wakefulness. In turn, sleep increases chromosome dynamics, which are necessary to reduce the amount of DSBs. These results establish chromosome dynamics as a potential marker to define single sleeping cells, and propose that the restorative function of sleep is nuclear maintenance.
阅读论文全文请访问:http://t.cn/EMvfAt1
期刊介绍:Nature Communications (https://www.nature.com/ncomms/) is an open access journal that publishes high-quality research from all areas of the natural sciences. Papers published by the journal represent important advances of significance to specialists within each field.
The 2017 journal metrics for Nature Communications are as follows:
•2-year impact factor: 12.353
•5-year impact factor: 13.691
•Immediacy index: 1.829
•Eigenfactor® score: 0.92656
•Article Influence Score: 5.684
(来源:科学网)
特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。